Table of contents
Introduction
Apache Spark is an open-source big data processing platform that can quickly and effectively process large datasets. Amazon S3 is one of the most popular large-data storage platforms. In this response, we will go over how to use Apache Spark to process data on Amazon S3.
The steps below describe how Apache Spark processes data on Amazon S3:
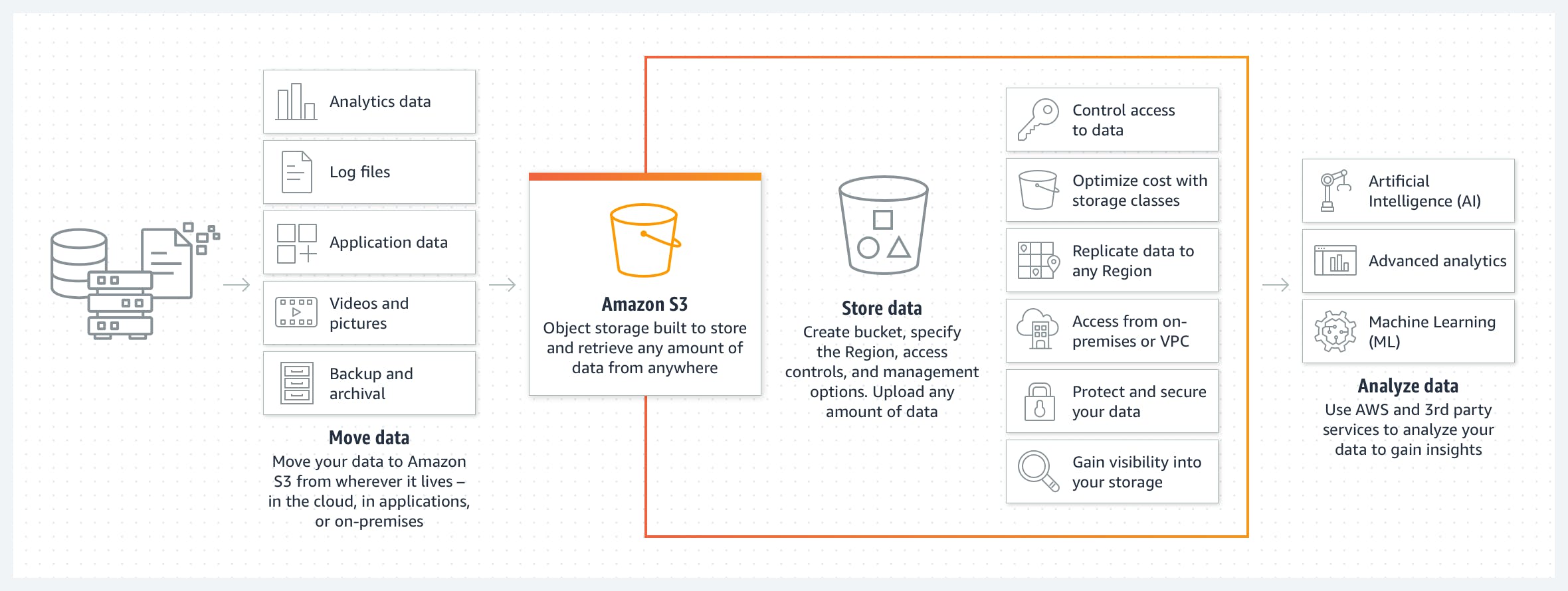
Setting up an S3 bucket: The first step is to create an S3 bucket for the data stored in your AWS account. Using the AWS interface or the AWS SDK, you may build an S3 bucket.
Uploading Data: The next step after setting up the S3 bucket is to upload the data you wish to use S3 to process. Any S3-compliant client, the AWS interface, or the AWS CLI can be used to upload data to S3.
The following step is to configure Apache Spark on your workstation or cluster. After that, you can use an AWS-managed service like Amazon EMR or download Spark from the Apache Spark website and install it yourself.
The following step is to use the SparkSession class to create a Spark session after setting up Spark.
The Spark session offers a streamlined way to communicate with Apache Spark.

Reading data from S3:
The next step is to read data from S3 using the SparkSession object. Finally, you can get data from S3 using the s3a:/ protocol, an S3A connector that lets Spark talk to S3.
Using Spark's transformation APIs, such as map, filter, and reduce, you may alter the data after reading it from S3.
Spark also has a lot of APIs that can be used to change data quickly and in many places.
Adding Data to S3:
The last step is to use the Spark write APIs to write the data back to S3 once it has been transformed. Again, any S3-compliant client or the s3a:/ protocol can be used to write data to S3.
Using Spark for Efficient Data Processing on Amazon S3
You may adhere to the following recommended practices to process data on Amazon S3 effectively with Spark:
Employ partitioning:
When partitioning data, it can be shared among many cluster nodes, improving performance. With the partition API, you may divide up data according to a key column.
Employ caching:
When you need to get the same information repeatedly, caching it in memory can help you do it faster. With the cache API, you can cache data.
Employ columnar formats:
Columnar formats like Parquet and ORC can improve the speed of reading and writing data because they compress and store data well.
Use compression:
Compression can improve performance by cutting down on the amount of data that has to be sent over the network.
Spark supports gzip, snappy, and other types of compression.
Conclusion
In conclusion,
Apache Spark offers a productive method for handling large amounts of data on Amazon S3.
Setting up an S3 bucket, uploading data, configuring Spark, starting a Spark session, reading data from S3, transforming data, and publishing data to S3 are all steps in processing data on S3 using Spark.
Use best practices, including partitioning, caching, columnar formats, and compression, to handle data effectively.
